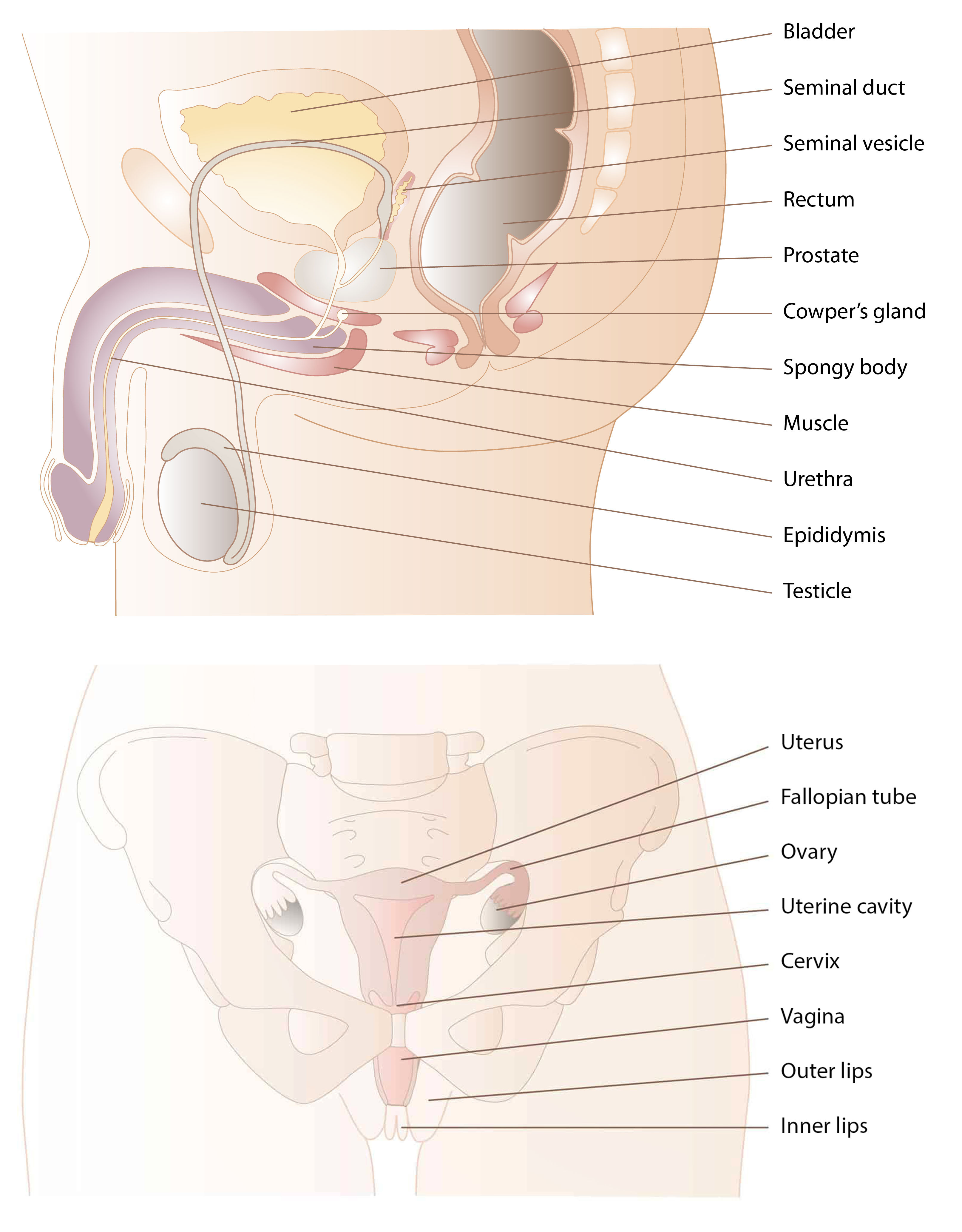
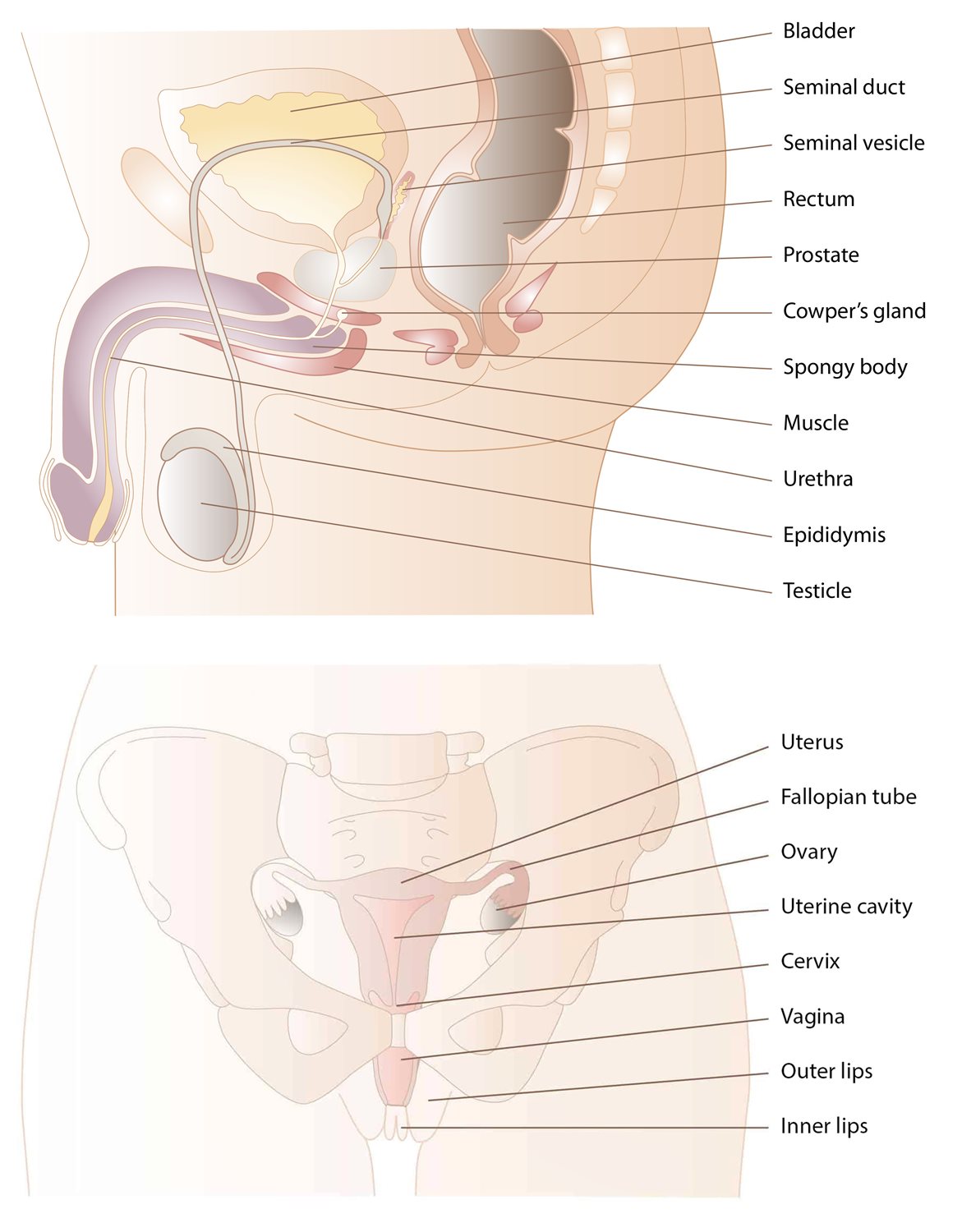
External genitalia
A man’s external genitalia (external genitals) consist of the penis and the scrotum. The penis contains three areas of spongy tissue that fill with blood when he has an erection. The urethra passes through one of these areas along the underside of the penis. The scrotum is a kind of skin bag containing the testicles (balls) and epididymides. Muscles in the scrotum can pull the testicles up nearer the body when it is cold, and release them down again when it is warm. The testicles produce sperm cells and the male sex hormone testosterone.
A woman’s external genitals consist of the outer and inner labia and the clitoris. The collective name for these is the vulva. The labia cover the vaginal opening and the urethral opening. Just as the man’s penis has areas of spongy tissue, the clitoris also has a corresponding area that fills with blood when the woman is sexually aroused. The woman also has spongy tissue on each side of the vaginal opening; they make the opening narrower when they fill with blood.
We are in the process of translating the full content of this website to English.
Translated material will be published consecutively as soon as it is ready.
There are about 1300 questions with answers, as well as many articles that need to be translated.
We ask for your patience and understanding for this.